NDT Written Practice: The Compliance Document That Protects Your Company
An NDT written practice is one of the most important documents supporting any nondestructive testing program. While it often sits behind the scenes, this document defines how inspection personnel are trained, qualified, certified, and evaluated. When one is missing, outdated, or poorly written, companies can face audit findings, rejected work, or serious challenges after a failure investigation.
Rather than being simple paperwork, a written practice provides the structure that connects industry standards to real-world inspection activities and quality systems.
What a Written Practice Covers in Nondestructive Testing
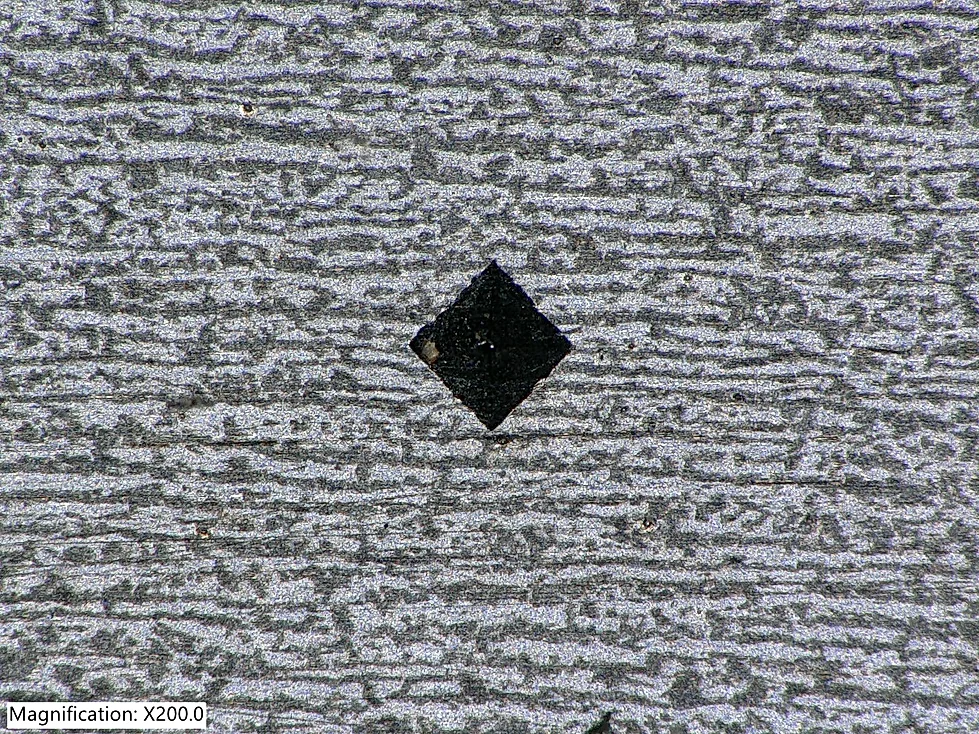
It outlines how nondestructive testing is performed in accordance with standards such as ASNT SNT-TC-1A or ANSI/ASNT CP-189. An NDT written practice establishes minimum training hours, experience requirements, examination criteria, certification authority, and documentation expectations for inspection personnel.
This document should reflect how inspections are actually performed, not just how standards describe them in theory. It defines which NDT methods are used, who is qualified to perform them, and how competency is verified and maintained. A well-developed written practice helps ensure consistency across projects, shifts, and inspectors.
Why They Matter for Compliance and Risk Management
Auditors, customers, and regulatory bodies frequently request documentation that shows how inspection personnel are qualified. Gaps are among the most common audit findings, especially when requirements for examinations, recertification intervals, or Level III oversight are unclear.
Beyond audits, written practices play a critical role when issues arise in the field. After a weld defect, material failure, or dispute, documentation is often reviewed to confirm that inspections were conducted by qualified personnel following documented procedures. Without a defensible NDT written practice, even properly performed inspections can be questioned.
Training, Qualification, and Certification Roles
Training and qualification requirements form the backbone of an NDT written practice. The document defines how Level I and Level II personnel are trained, examined, and certified under the technical direction of a Level III.
A compliant program typically documents:
- Required classroom and practical training hours
- Experience thresholds for each NDT method
- Written, practical, and vision examination requirements
- Certification duration, renewal criteria, and record retention
Clear definitions help eliminate confusion and ensure inspection results can withstand scrutiny from auditors or clients.

Common Issues Identified During Audits and Reviews
Many organizations have documentation in place but are unaware of its weaknesses until an external review takes place. During audits, several recurring issues tend to surface that can put compliance and inspection credibility at risk.
Common findings include:
- Outdated standards references
An NDT written practice may cite superseded codes or older revisions that no longer reflect current requirements. - Incomplete qualification details
Training hours, experience requirements, or examination criteria may be unclear or insufficiently documented. - Mismatch between documentation and practice
When inspections differ from what is documented, the written practice loses its value during audits or investigations. - Unclear certification authority
They may not clearly identify Level III responsibility or who is authorized to certify personnel. - Administrative gaps
Missing signatures, recertification intervals, or incomplete records can weaken an inspection program.
These issues are often unintentional and typically result from documentation that has not been reviewed as operations evolve.
Keeping Current and Defensible
An effective NDT written practice should be reviewed regularly and updated when standards change, new methods are introduced, or personnel responsibilities shift. Treating it as a living document helps maintain compliance while supporting consistent inspection quality.
Regular review also helps identify gaps before they surface during audits or client reviews, reducing the risk of corrective actions or delays. At WJMG, written practices are developed to reflect real testing environments while aligning with applicable standards. A well-maintained NDT written practice supports qualified inspectors, defensible results, and long-term confidence in nondestructive testing programs.